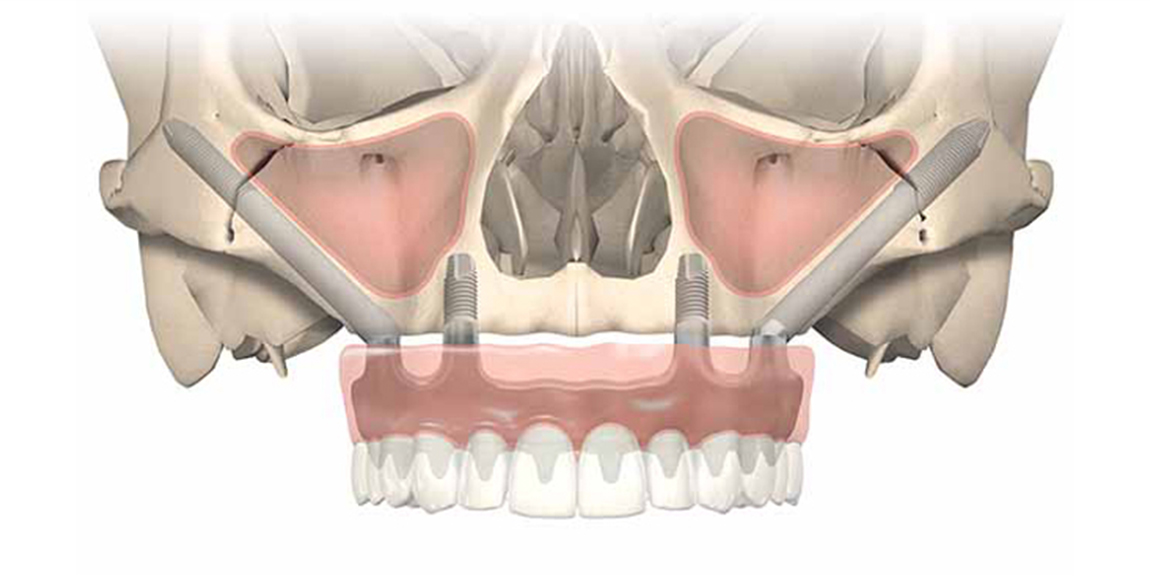
Peri-Implantitis – The main adversary for dental implants
Replacing a missing tooth with dental implants is not a new thing. Even though the porcelain crowns implanted with a titanium post into the jawbone cannot be infected, the tissues surrounding the implants are prone to infection.
If any infection in the gum tissues around the implants are not treated properly, the contamination will advance and cause Peri-Implantitis.
What is Peri-Implantitis?
Peri-Implantitis – The main culprit for dental implants. The gum disease that causes mucositis in the gum tissues around the inserted false teeth. This is followed by an inflammation in the gum regions around the implant and gum recession. It progresses to wipe out the underlying bone that ensures the implant. Sometimes, poor workmanship in fixing tooth implants also make it a haven for bacterial colonization and lead to the implant infection followed by Peri-Implantitis.
Teeth implants are highly vulnerable to this infectious disease because the fake tooth inserted does not have the microbial agents possessed by a natural tooth. Unlike natural teeth, the implants do not have a direct connection with the immune system. Hence they cannot fight against the bacteria colonized in the thin biofilm (Plaque) developed around an implant.
Thus the infection develops to cause peri-implantitis and lead to implant failure.
What are the symptoms of Peri-Implantitis?
Certain symptoms that are ideal to periodontal diseases are also the warning signals for this issues. Otherwise, the sufferer cannot see any direct symptoms even after the infection deteriorates the bone as bone loss is painless. Few signs shown by the mucosa include:
- Gum bleeding
- Inflammation around the implants
- Recession in gums that expose the metal thread of the implant
- Deep pockets developed around the implant
- Implant mobility
Dental Health Specialists say that this might occur immediately after the implantation or after a few years. It means not all the implants have the risk of peri-implantitis. This infection is rare and chances are higher for people who have gum diseases, osteoporosis, diabetes and smoking. Similarly, people who have disorders like soft bone are susceptible to the disease.
What are the treatment options?
Initially, the dental disease is hard to diagnose and treatable. The advancements in Dentistry bring various treatment options to cure this disease.
If the disease is identified in the initial stage, it can be treated by cleaning the infected area. Besides this, antibiotics are also powerful to treat the issue. Likewise, Conservative Therapy and other non-surgical procedures like laser treatment also provide fruitful results in peri-implantitis treatment.
In contrast, the sufferer will require surgical procedures if the infection is found after penetrating the bone. In such cases, the implant is removed and then reinserted after the bone grafting surgery. Dentists also assure that the success rates of peri-implantitis treatment are higher for such surgical regeneration procedures.
Conclusion
As mentioned earlier, the disease does not show any sign of infection. Hence regular dental visits to assess the dental implants is essential. It will help to diagnose the infection in the initial stages.
Don’t ignore minor issues like bleeding, redness and swelling in gums around the implants. Visit your Dentist or Implantologist immediately.
Take care of the dental implants similar to caring your natural teeth. Efficient brushing and flossing to extract the particles deposited on the implant will help you to stand far away from peri-Implantitis.